Pigmentary Dispersion Syndrome Treatment
Pigmentary dispersion syndrome treatment. Laser iridectomy eliminates the iris concavity in most patients with pigment dispersion syndrome by permitting equalization of pressures between the. Laser peripheral iridotomy PI has been proposed as a treatment for pigmentary glaucoma PG and pigment dispersion syndrome PDS by reducing the dispersion of pigment. Laser surgery has a limited role in the management of these entities whereas trabeculectomy remains an.
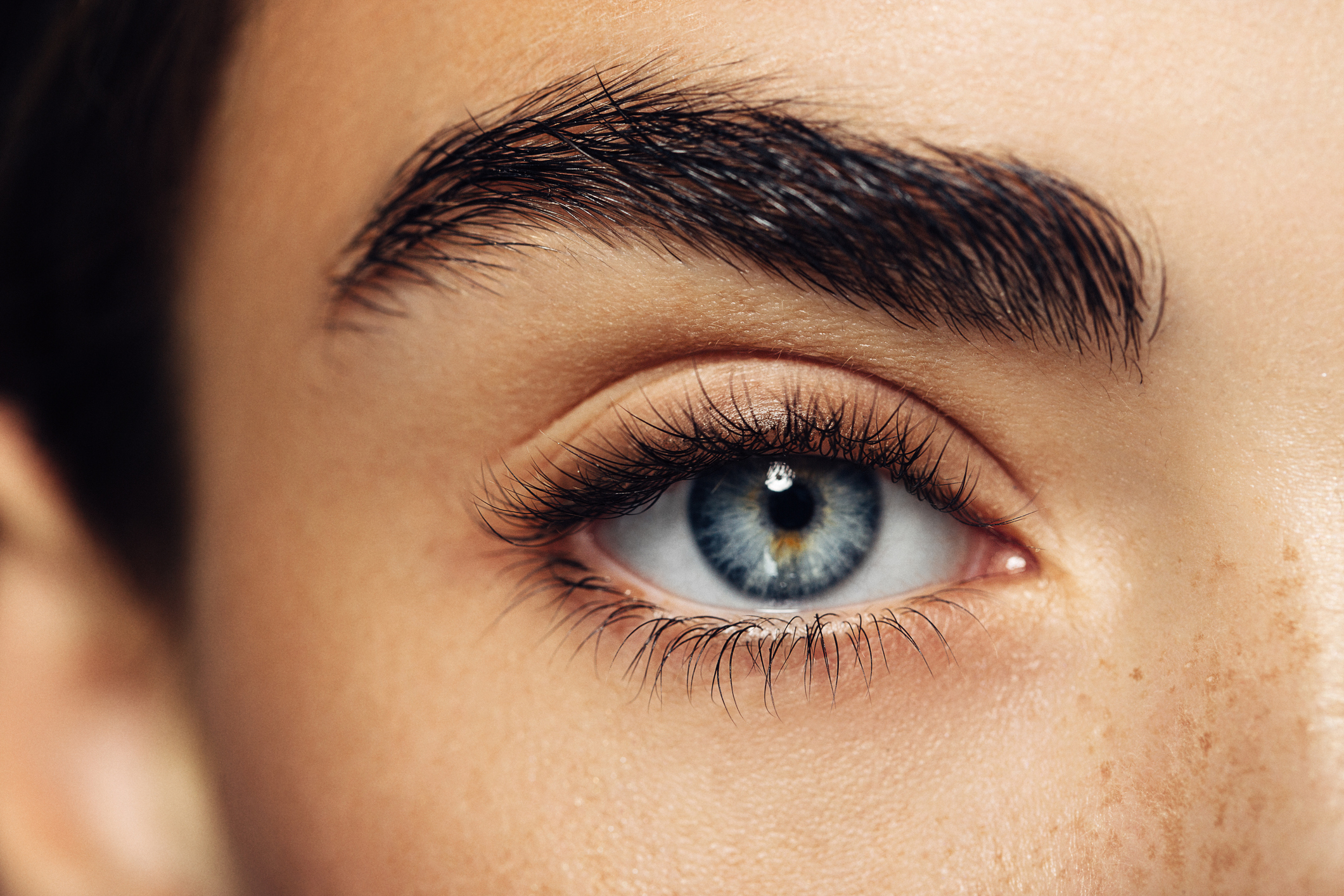
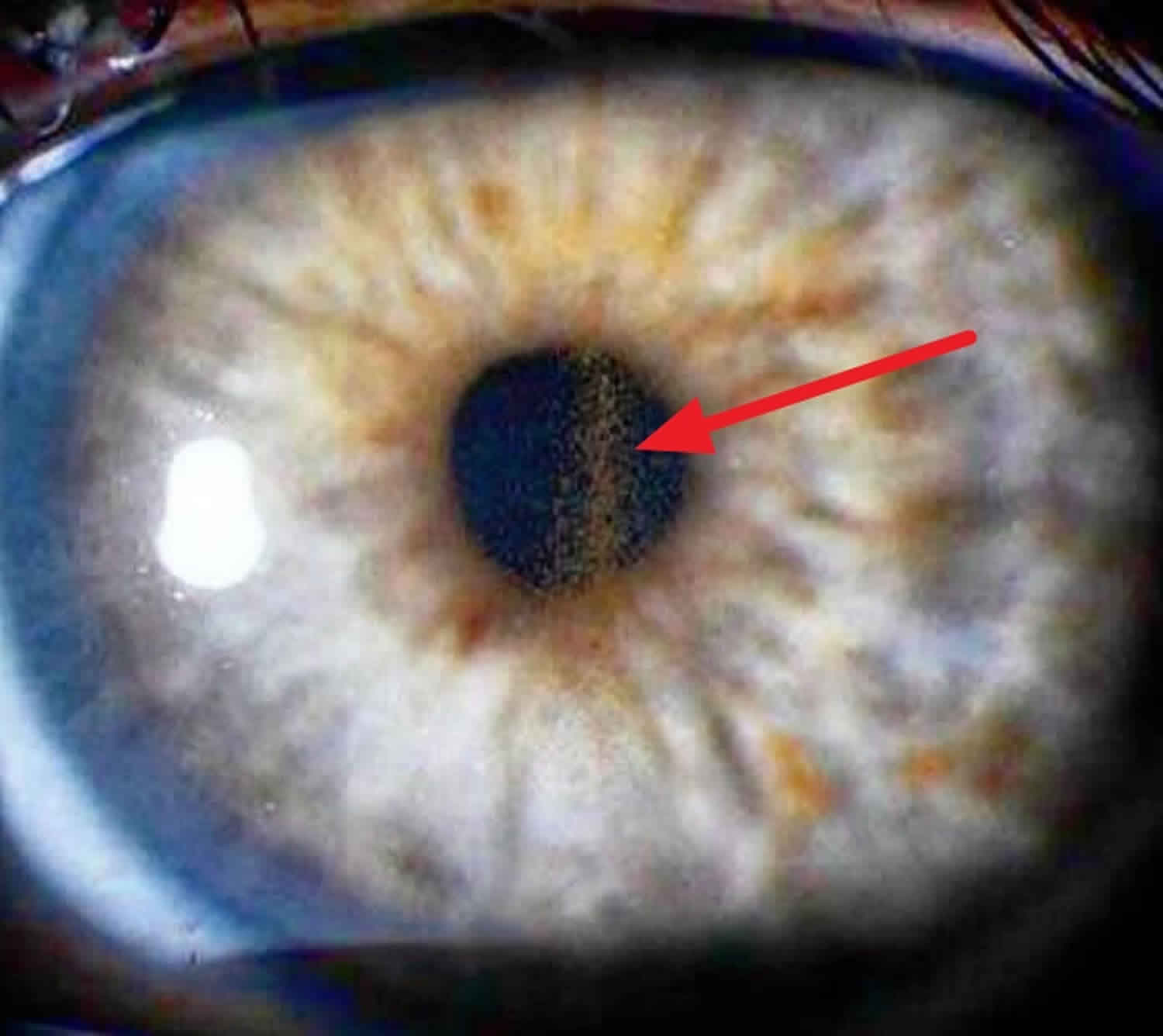
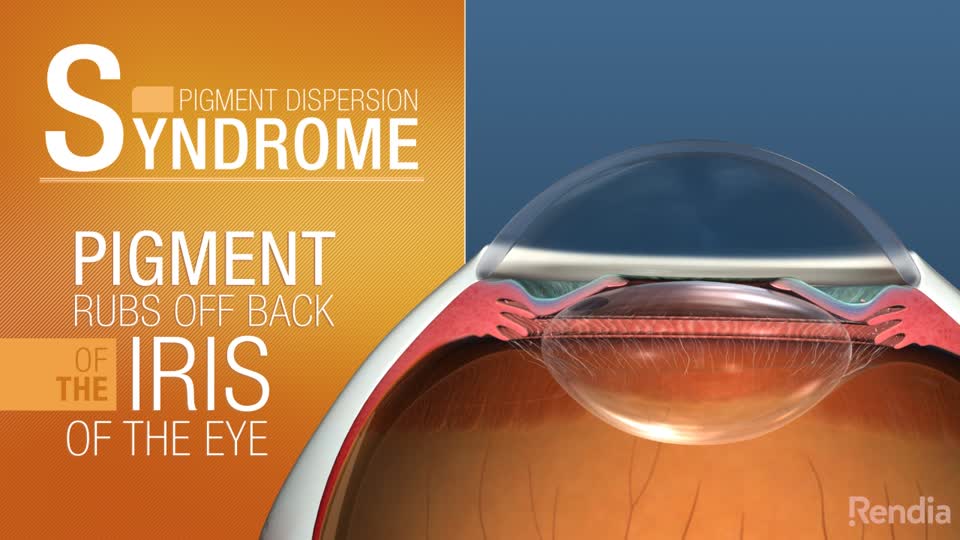
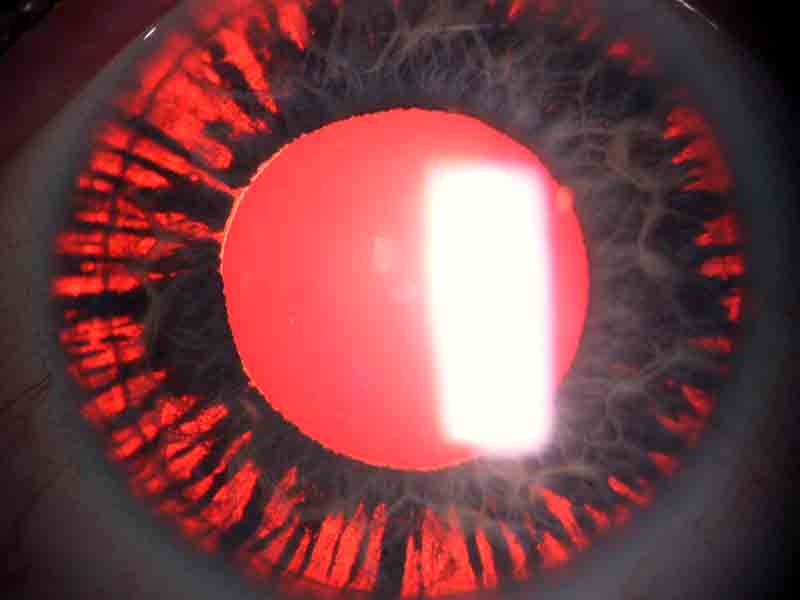
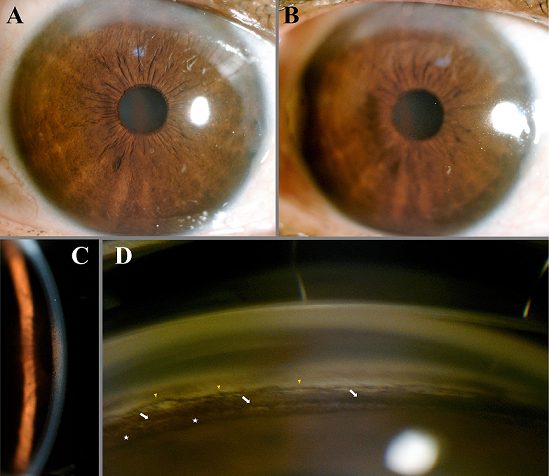
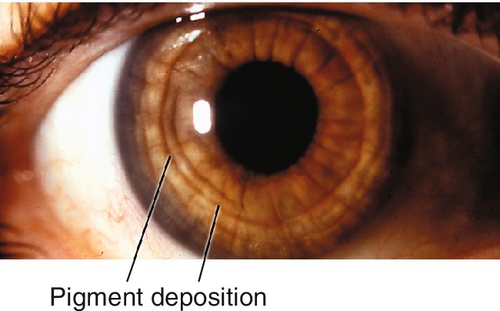
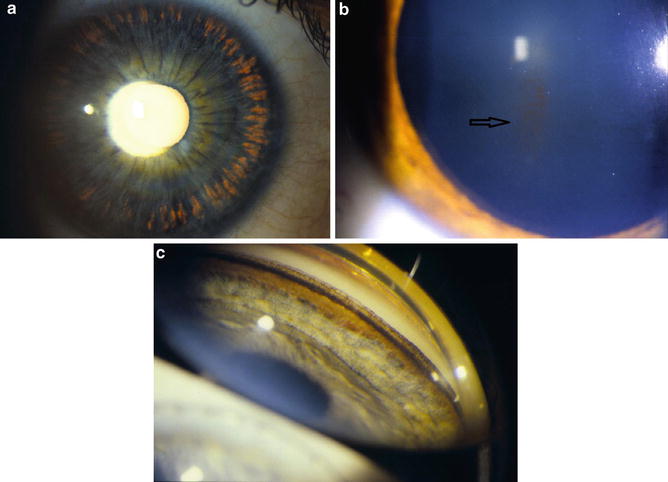
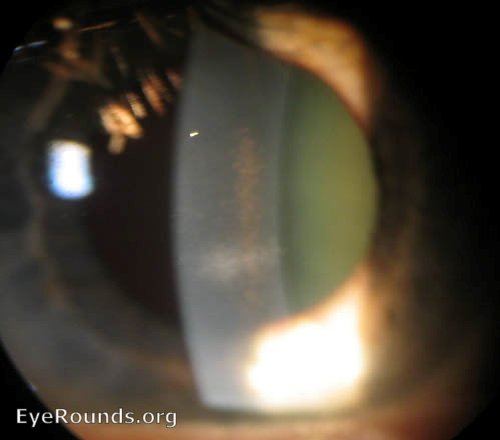
Pigmentary glaucoma results from zonular-pigment dispersion primarily in young myopic white individuals. For pigment dispersion syndrome. Pigment dispersion syndrome is a condition in which friction between the posterior surface of the iris making contact with the anterior zonules of the lens releases pigment and cells from the iris debris that is flushed into the anterior chamber and the trabecular meshwork where it may become trapped in the drainage pathway.
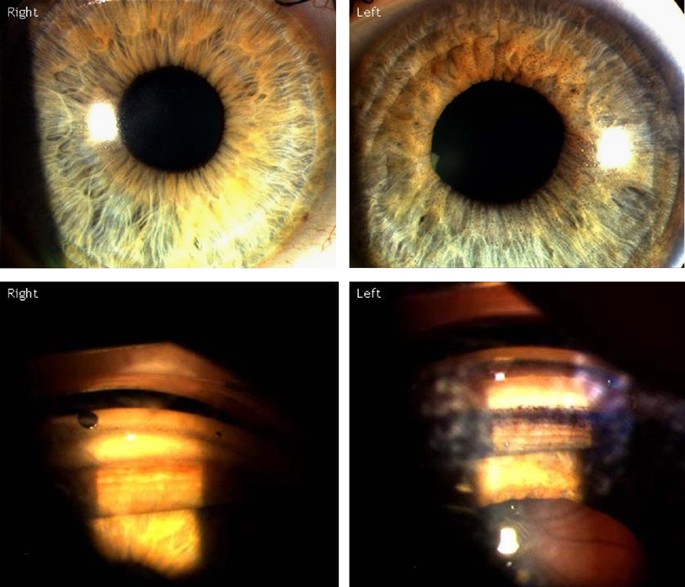
Laser iridotomy located with transillumination is recommended as the treatment for iris-zonular rubbing in PDS and PG caused by reverse pupillary block. Regular eye check from a doctor Beta blockers are prescribed to reduce the increased pressure present in the eye. Or 2 malignantly elevating the intraocular pressure.
This may explain why treatments directed at trabecular outflow such as laser trabeculoplasty are more effective in the earlier stages of pigmentary glaucoma 14. Literature from the review period has further defined the unique clinical characteristics of pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma. Accommodation and iridotomy in the pigment dispersion syndrome.
Pigment-dispersion syndrome can be treated with eye drops or other medications. A new mechanism concept a new treatment and a new technique. The treatment of pigmentary glaucoma involves lowering eye pressure by using medications laser or surgery which is similar to the treatment options for open-angle glaucoma.
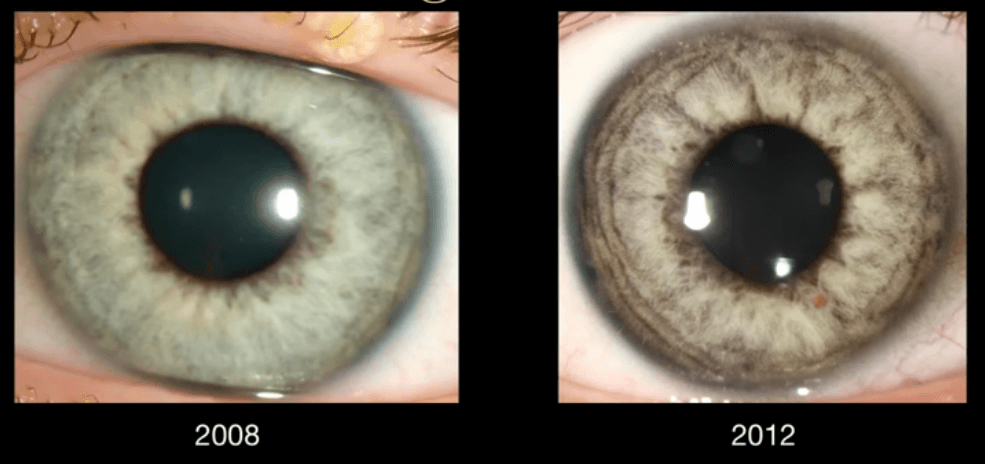
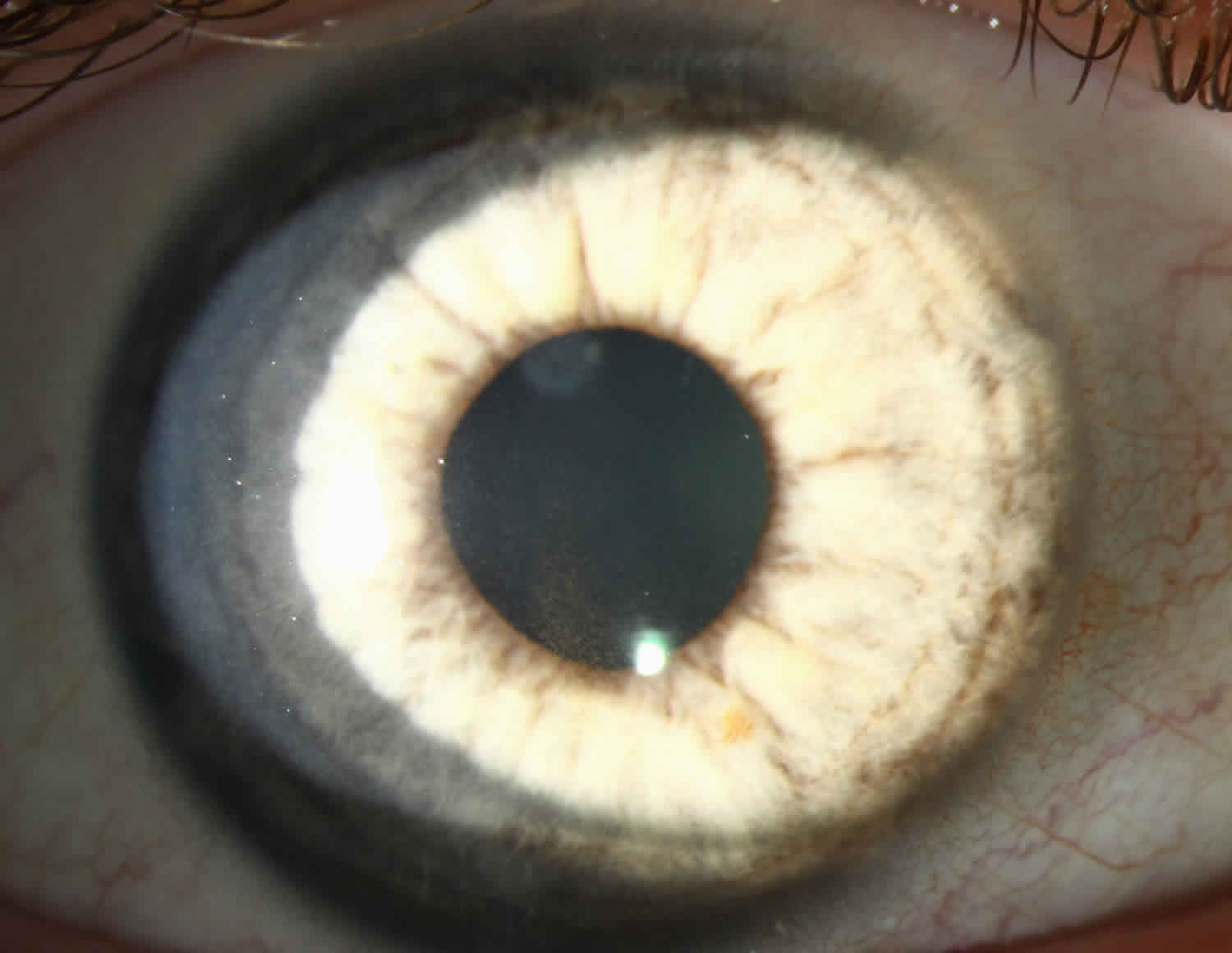
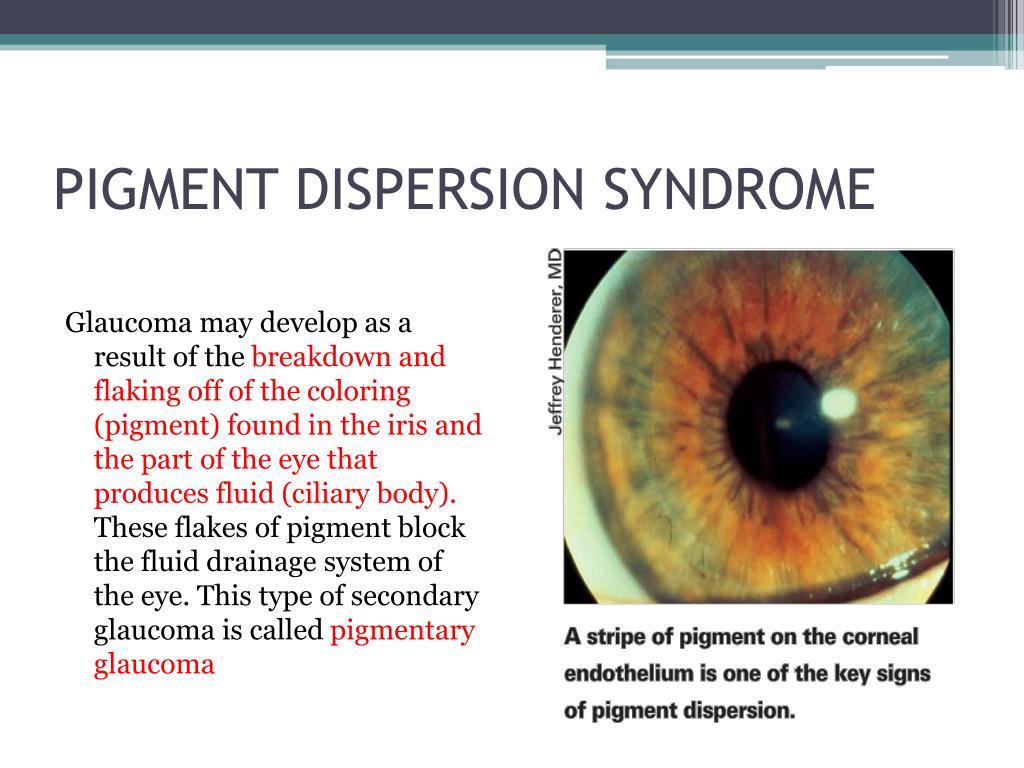
Pigment dispersion syndrome PDS is an eye disorder that can lead to a form of glaucoma known as pigmentary glaucomaIt takes place when pigment cells slough off from the back of the iris and float around in the aqueous humorOver time these pigment cells can accumulate in the anterior chamber in such a way that they begin to clog the trabecular meshwork the major site of aqueous humour. Many patients with pigment dispersion syndrome will develop high eye pressures and about half of those who develop high eye pressure will develop glaucoma. 1 benignly not affecting the intraocular pressure as in pigment dispersion syndrome.
Loss of peripheral vision Advanced. Literature from the review period has further defined the unique clinical characteristics of pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma.
Released pigment is carried to the trabecular meshwork where it resides.
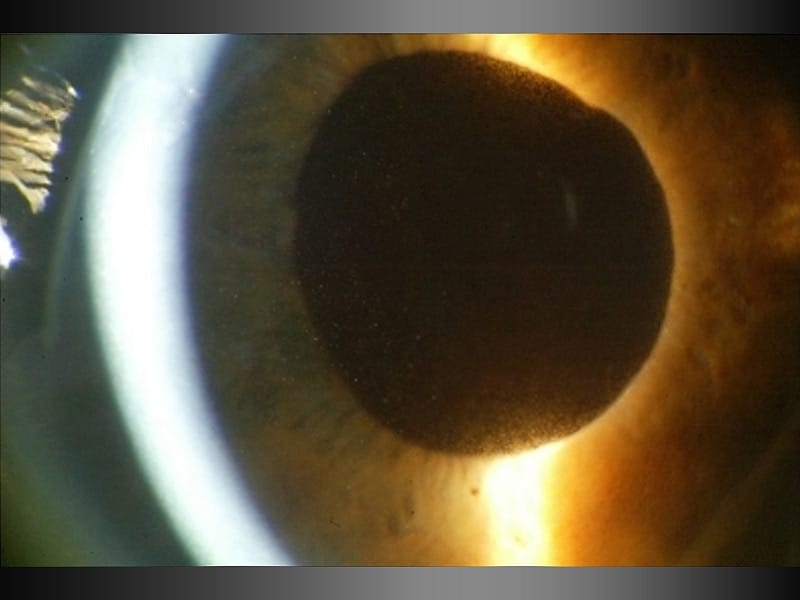
The concavity of the midperipheral iris allows iridozonular contact. Regular eye check from a doctor Beta blockers are prescribed to reduce the increased pressure present in the eye. Pigment dispersion syndrome tends to affect relatively young people 20-45 most commonly Caucasians and those who are nearsighted. The goal of this review was to assess the effects of PI for PDS and PG. Pigment dispersion syndrome is a condition in which friction between the posterior surface of the iris making contact with the anterior zonules of the lens releases pigment and cells from the iris debris that is flushed into the anterior chamber and the trabecular meshwork where it may become trapped in the drainage pathway. Pigmentary glaucoma results from zonular-pigment dispersion primarily in young myopic white individuals. Medication The usual medications that lower eye pressure for open-angle glaucoma are also used for pigmentary glaucoma. Loss of peripheral vision Advanced. Many patients with pigment dispersion syndrome will develop high eye pressures and about half of those who develop high eye pressure will develop glaucoma.
Laser iridotomy located with transillumination is recommended as the treatment for iris-zonular rubbing in PDS and PG caused by reverse pupillary block. Or 2 malignantly elevating the intraocular pressure. The treatment of pigmentary glaucoma involves lowering eye pressure by using medications laser or surgery which is similar to the treatment options for open-angle glaucoma. CLINICAL FEATURES SYMPTOMS Early. Laser iridotomy located with transillumination is recommended as the treatment for iris-zonular rubbing in PDS and PG caused by reverse pupillary block. Laser surgery has a limited role in the management of these entities whereas trabeculectomy remains an. Literature from the review period has further defined the unique clinical characteristics of pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma.


























Post a Comment for "Pigmentary Dispersion Syndrome Treatment"