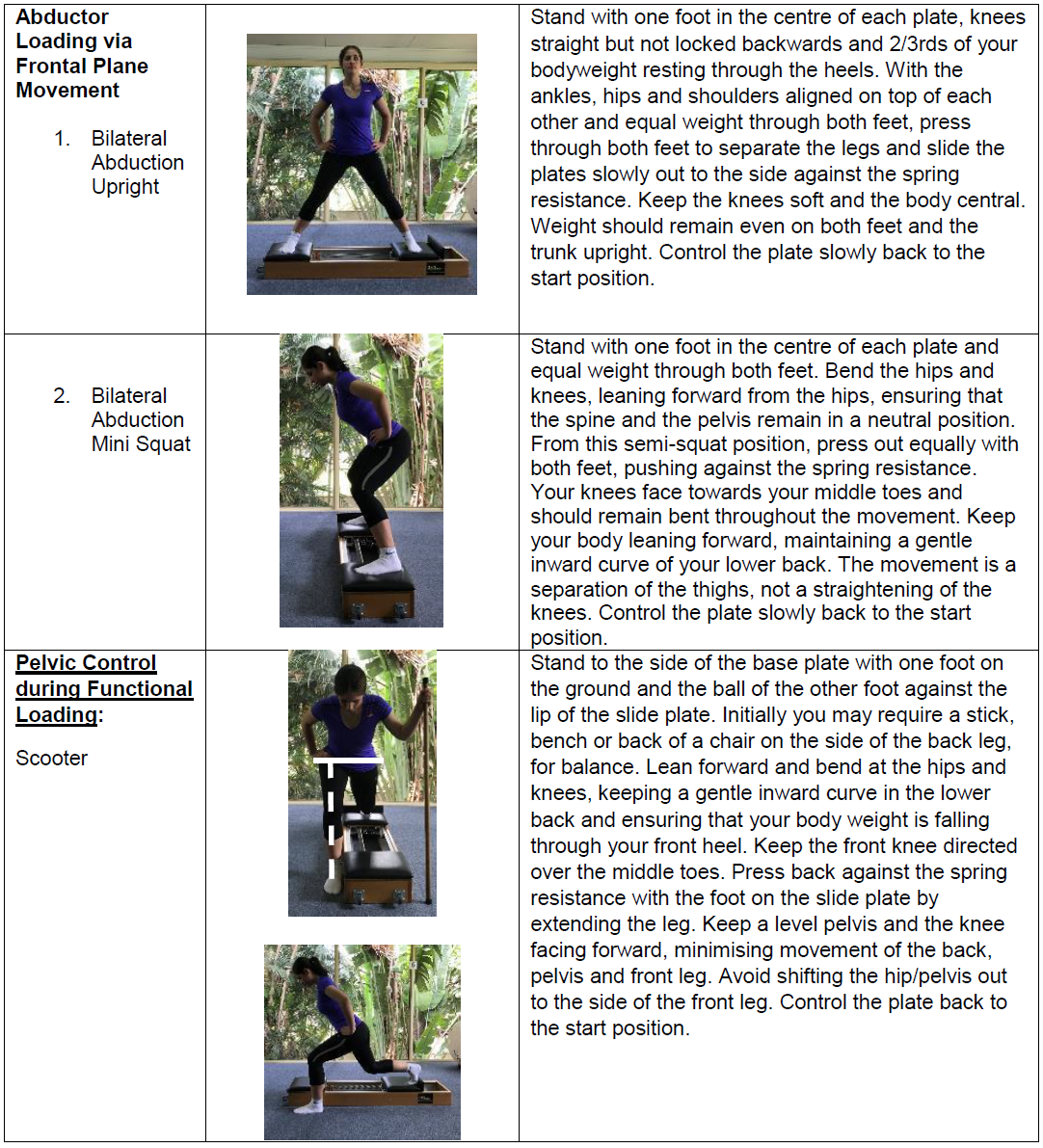
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome Prognosis
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome prognosis. Also known as greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS it is a common condition and easily treatable. Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome ICD 9 Codes. Lateral hip pain or greater trochanteric pain syndrome is a commonly seen condition.
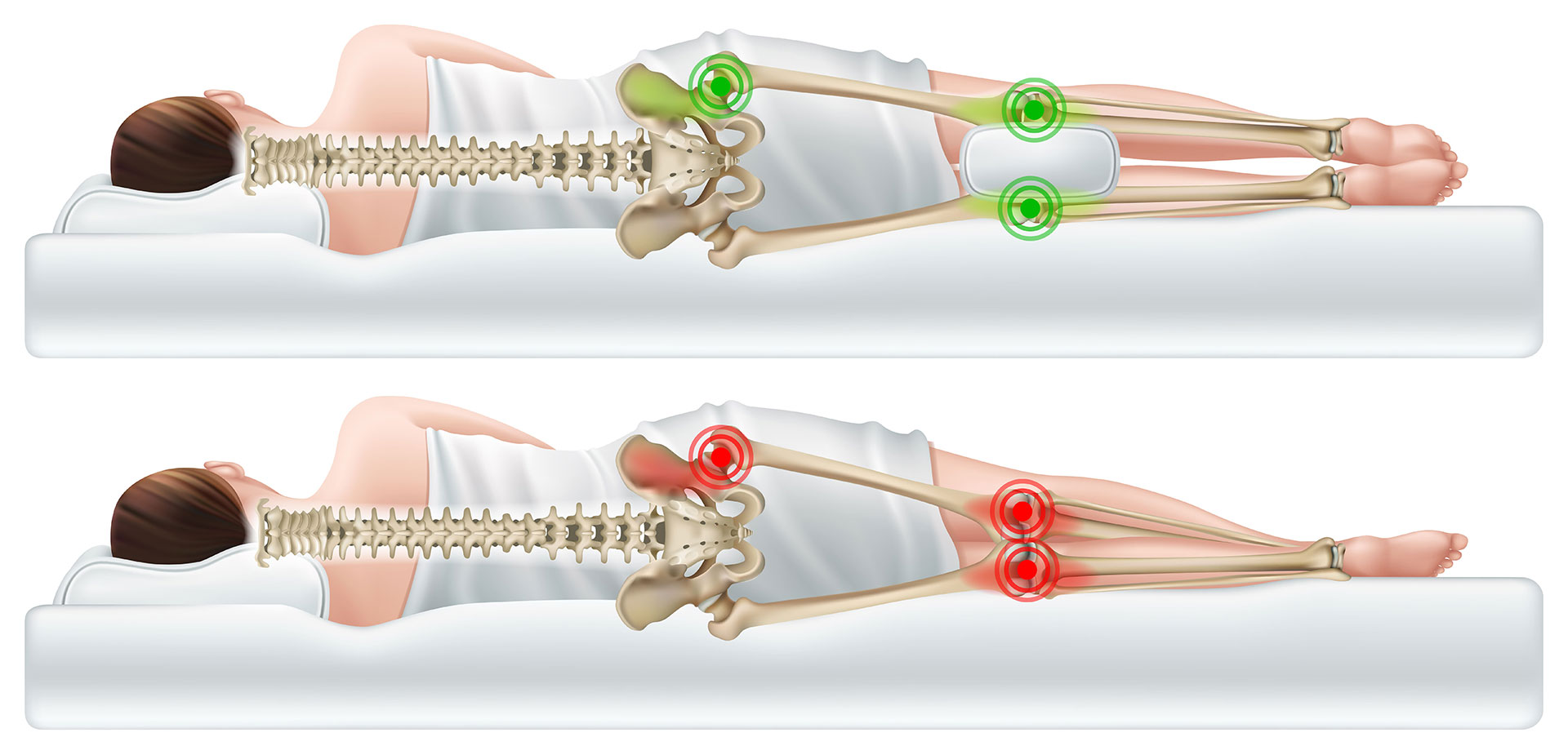
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome involves pain in the side of the hip thought to be due to overuse and inflammation of the muscles tendons and other structures in the side of the hip. Sometimes it may travel down as far as the outside of the knee. Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment.
Thus people with this condition may be labeled malingerers or may undergo many ineffective treatments due to misdiagnosis. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS is pain that occurs on the outside of the hip. The use of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of greater trochanteric pain syndrome.
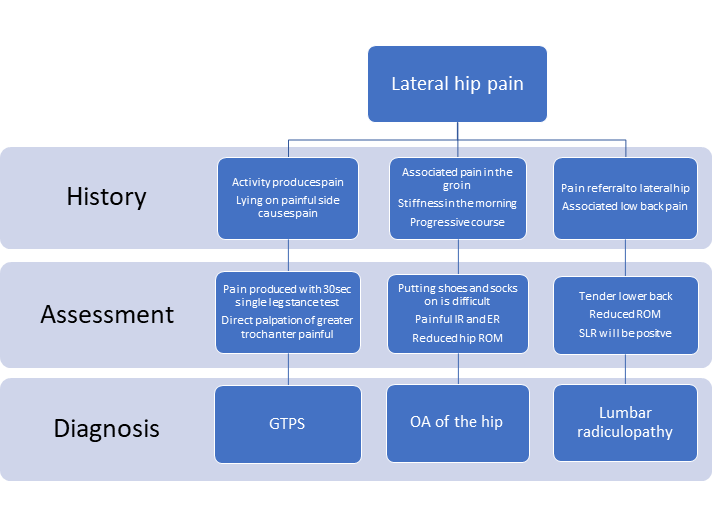
Localised lateral hip pain with focal point tenderness over the greater trochanter has for many years been clinically diagnosed as trochanteric bursitis1 2 The diagnosis of trochanteric bursitis may be inappropriate given that three of the four cardinal signs of inflammation. GTPS is more common in. A systematic literature review.
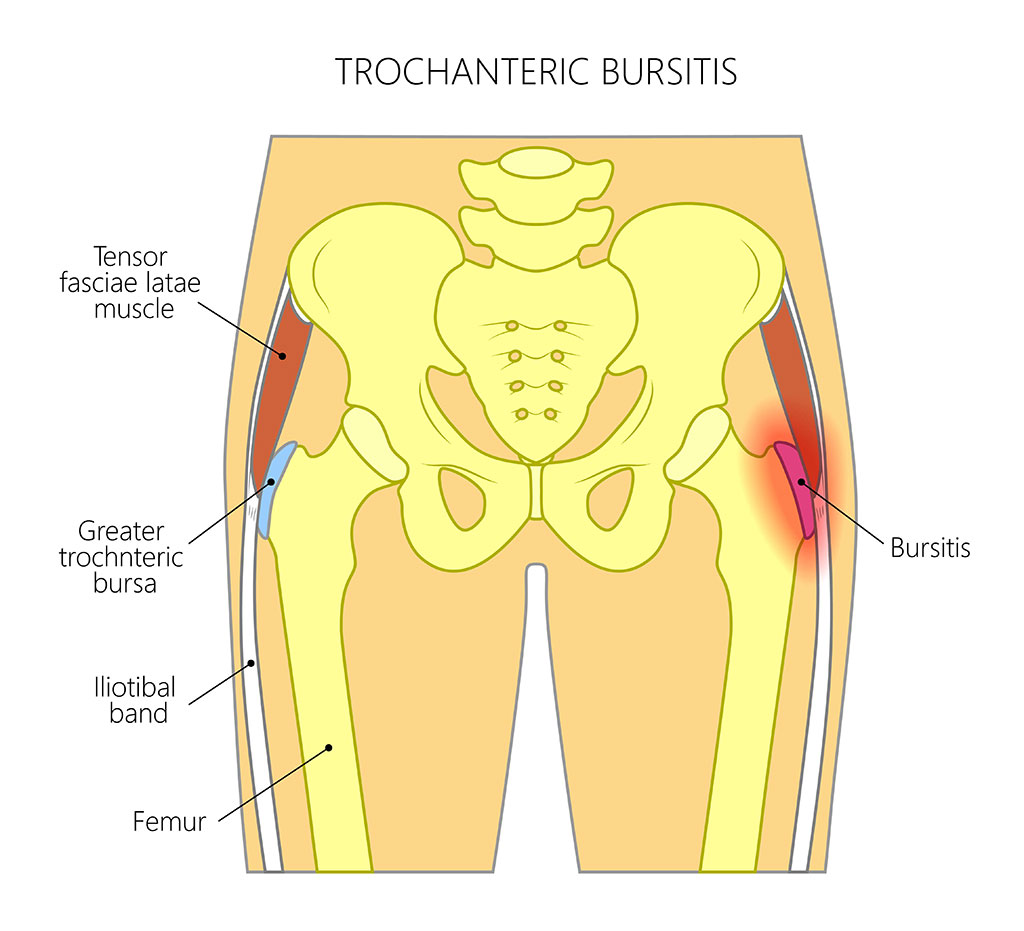
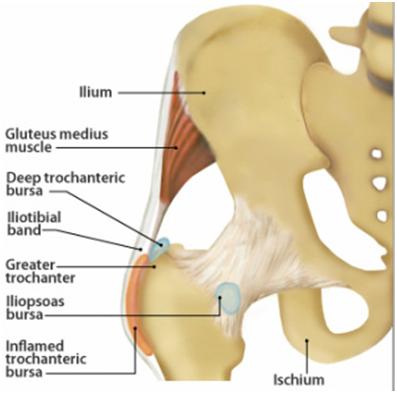
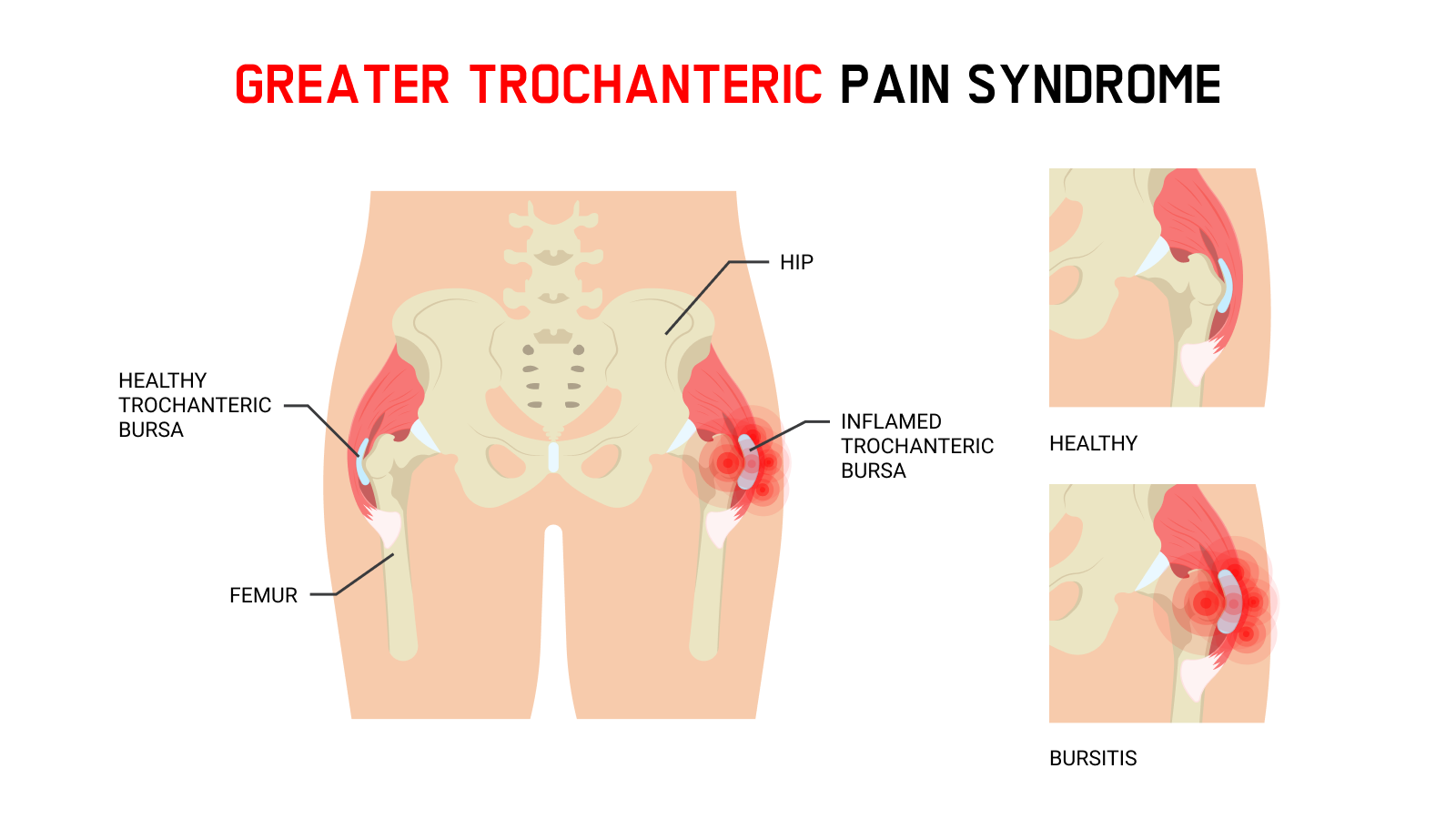
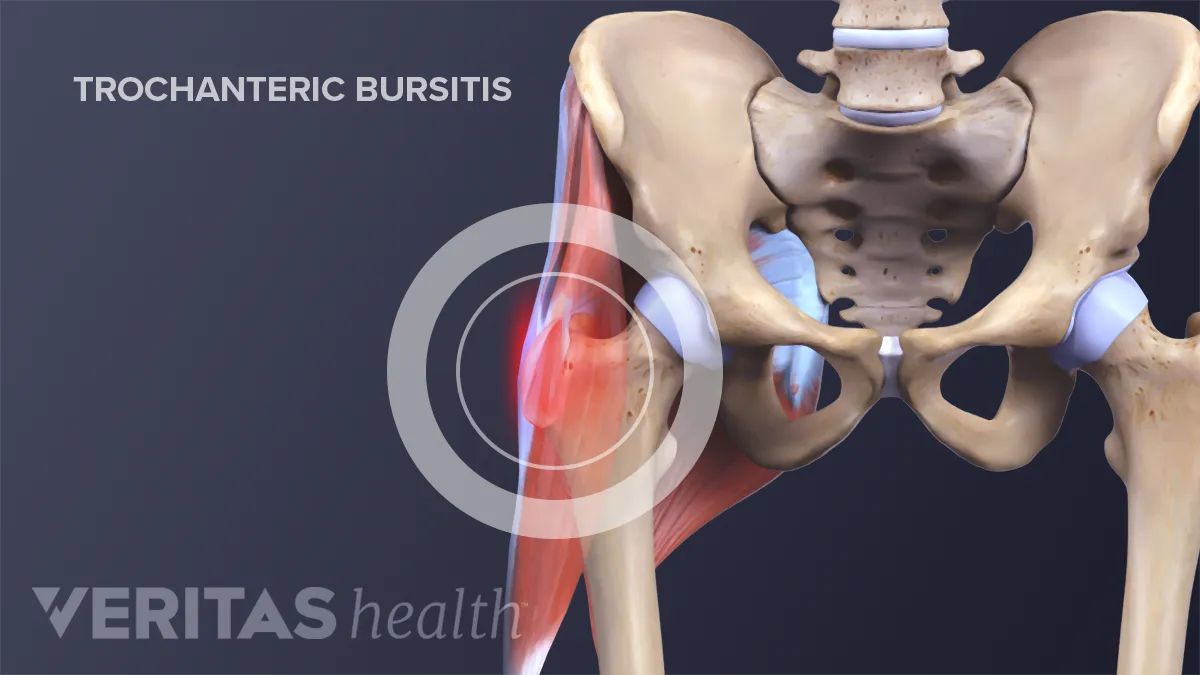
When this bursa becomes irritated or inflamed it causes pain in the hip. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS is a term used to describe chronic pain overlying the lateral aspect of the hip. Definition-Trochanteric bursitis is a regional pain syndrome that presents typically for outpatient physical therapy evaluation and treatment at a subacute or chronic stage.
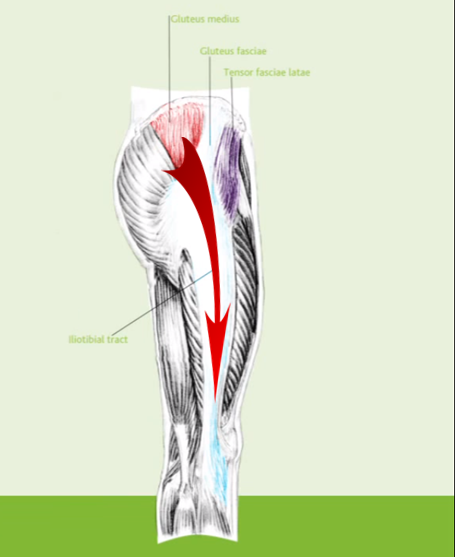
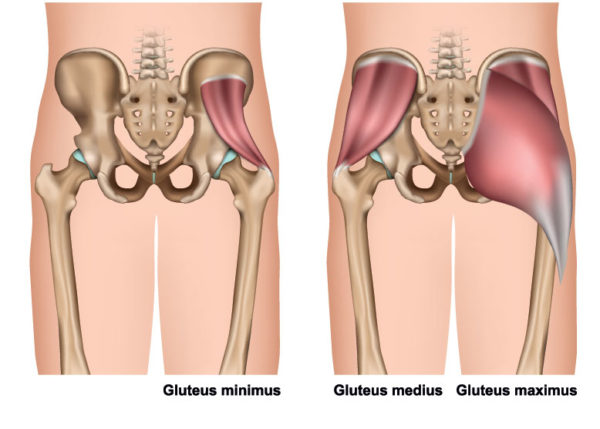
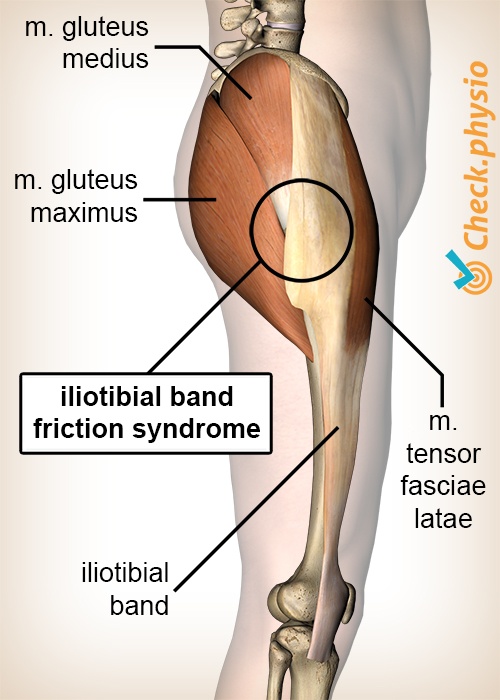
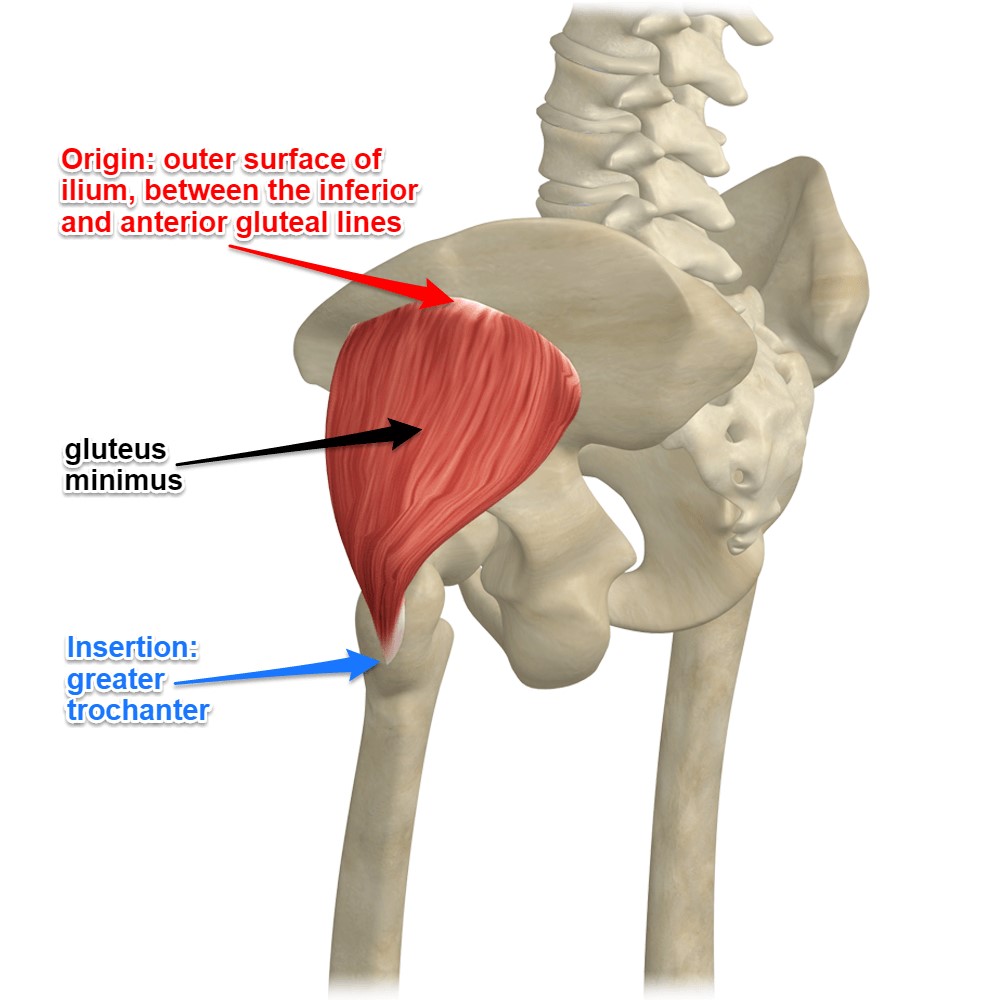
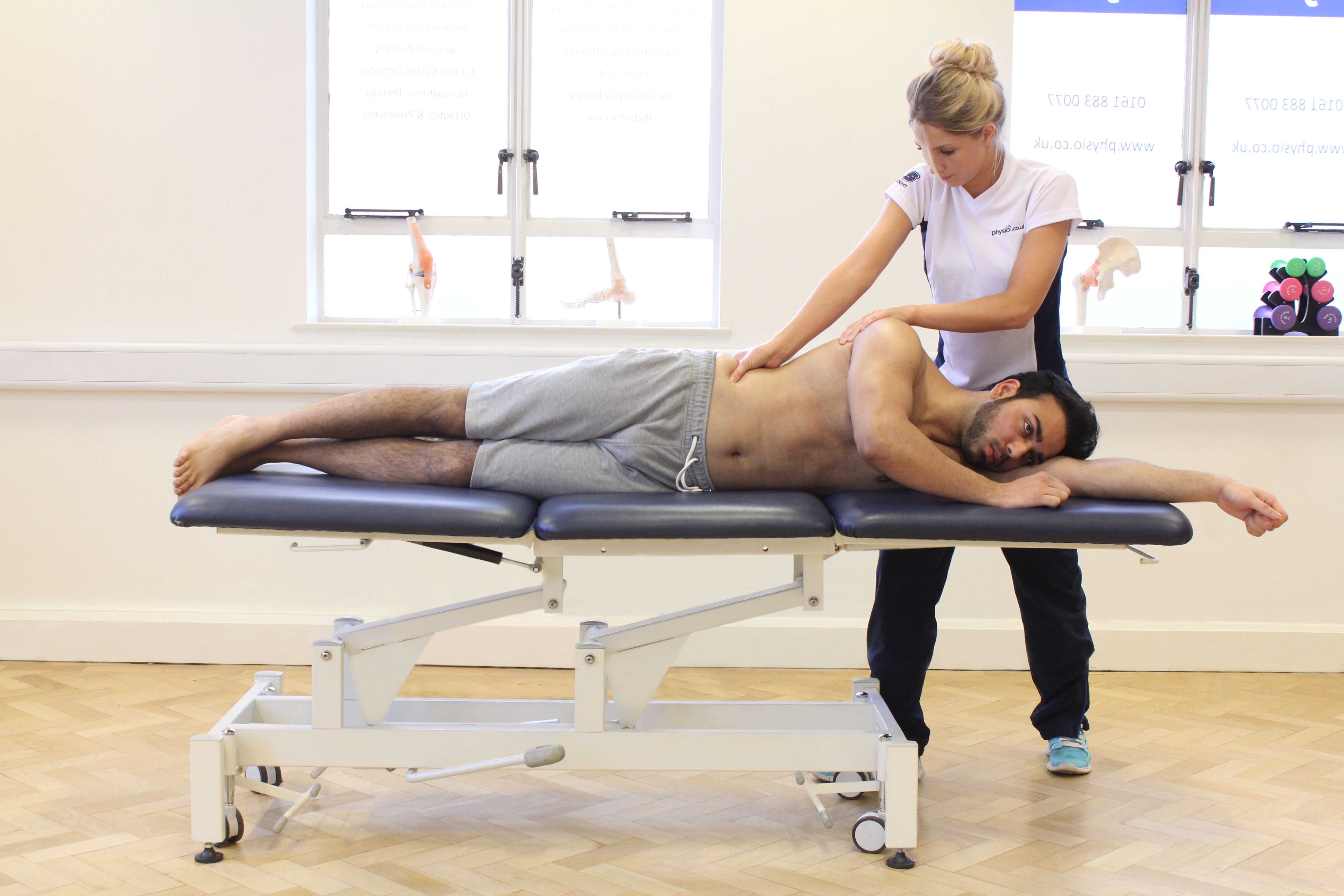
Two muscles in the side of the hip the gluteus medius and the gluteus minimus are involved in lifting the leg sideways and stabilizing the hip. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS previously known as trochanteric bursitis affects 18 per 1000 patients annually. With the help of physiotherapy and exercise they come back to normal life within a few months.
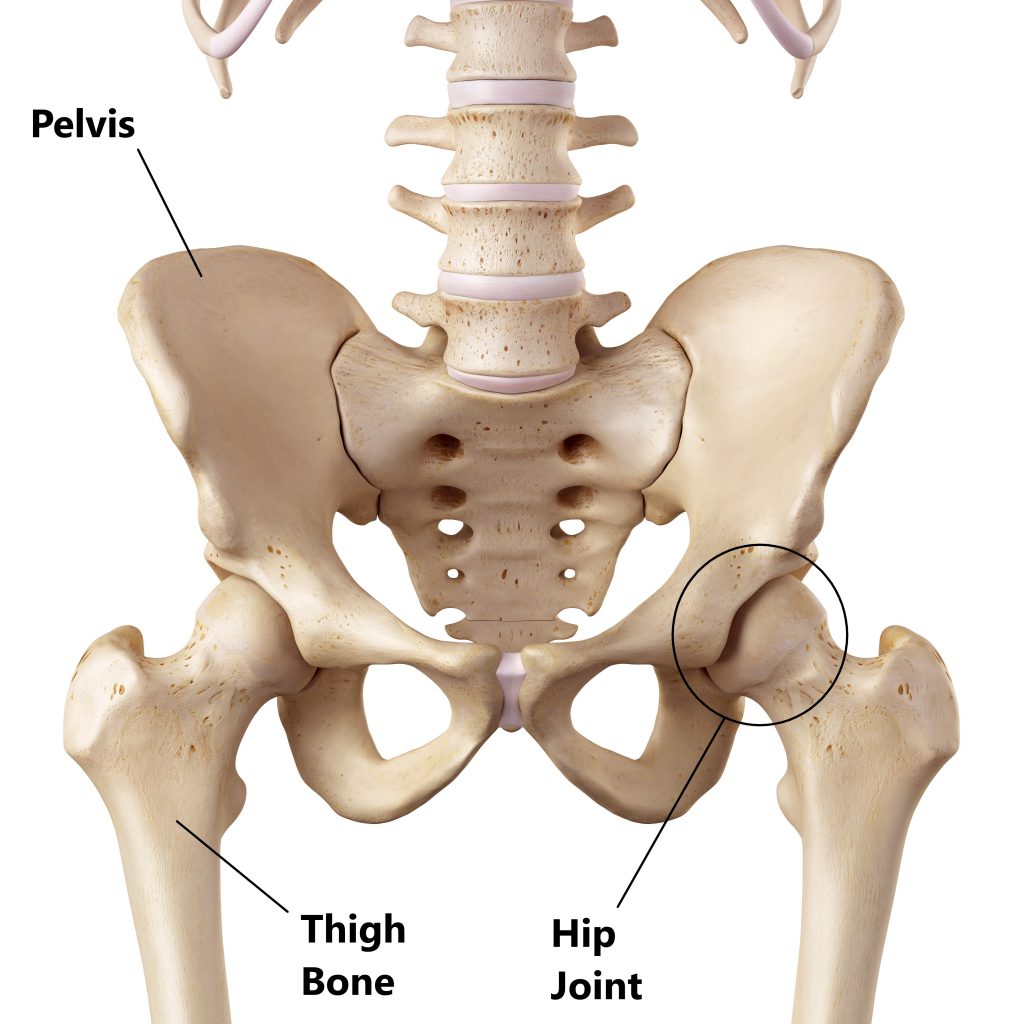
1 2 GTPS is the cause of hip pain in 1020 of patients presenting with hip pain to primary care with an incidence of 18 patients per 1000 per year. The definition of greater trochanteric pain syndrome is hip pain due to irritation of structures near the greater trochanter.
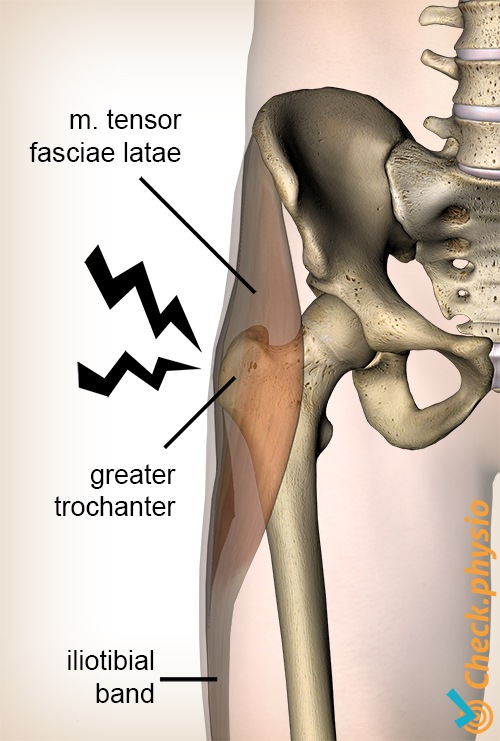
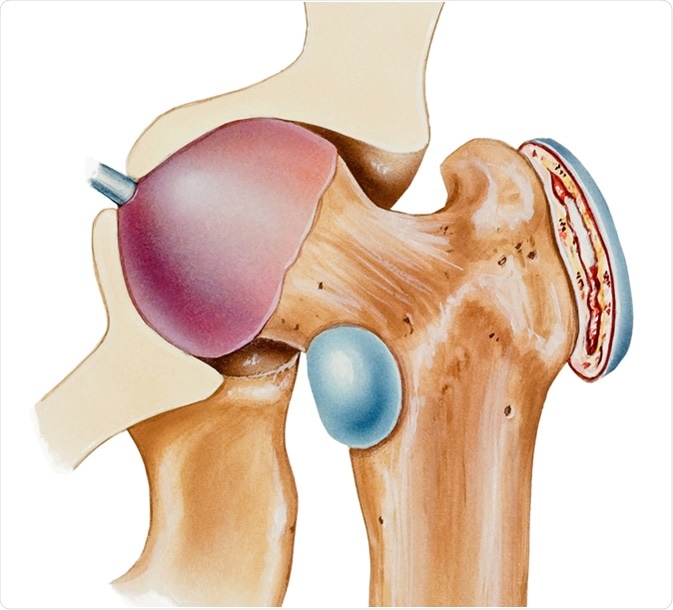
Trochanteric bursitis is inflammation swelling of the bursa fluid-filled sac near a joint at the outside lateral point of the hip known as the greater trochanter.
Localised lateral hip pain with focal point tenderness over the greater trochanter has for many years been clinically diagnosed as trochanteric bursitis1 2 The diagnosis of trochanteric bursitis may be inappropriate given that three of the four cardinal signs of inflammation. Two muscles in the side of the hip the gluteus medius and the gluteus minimus are involved in lifting the leg sideways and stabilizing the hip. A systematic literature review. Rubor erthythema and oedema are uncommon with only pain being a feature3 4 Radiological. Sometimes it may travel down as far as the outside of the knee. Cleveland Clinic is a. With the help of physiotherapy and exercise they come back to normal life within a few months. Traditionally greater trochanteric pain syndrome was thought to be due to inflammation of the greater trochanteric bursa. Also known as greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS it is a common condition and easily treatable.
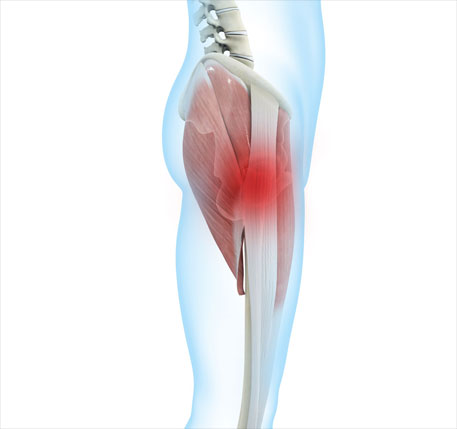
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS is pain that occurs on the outside of the hip. This regional pain syndrome once described as trochanteric bursitis often mimics pain generated from other sources including but not limited to myofascial pain degenerative joint disease and spinal pathology. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America 279-289. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS also known as lateral hip pain or trochanteric bursitis is a common condition where you can experience pain and tenderness on the outside of the hip and buttock region shown in the picture below. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome GTPS is pain that occurs on the outside of the hip. 4 However imaging studies microscopic examination and surgeries have shown otherwise. Localised lateral hip pain with focal point tenderness over the greater trochanter has for many years been clinically diagnosed as trochanteric bursitis1 2 The diagnosis of trochanteric bursitis may be inappropriate given that three of the four cardinal signs of inflammation.





















Post a Comment for "Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome Prognosis"