Chronic Disease Vs Infectious Disease
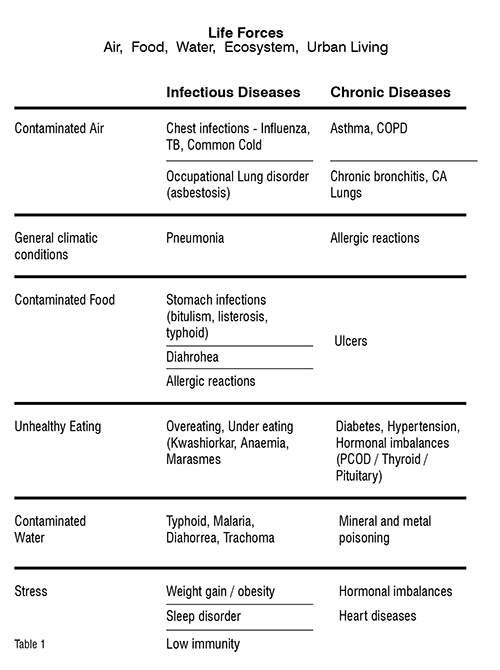
Chronic disease vs infectious disease. Diabetes occurred most frequently 409 followed by COPD 328 stroke 96 CHF 82 MI 59 and lung cancer 26. Though there have been observed associations between chronic disease and infectious disease since the beginning of epidemiological research increased emphasis on this relationship began in the late 1970s when new associations between specific infectious and chronic diseases were observed. Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic organisms or infectious particles while chronic diseases are not usually due to pathogens.
1 Many chronic diseases have an infectious origin such as cervical cancer human papillomavirus HPV and liver cancer hepatitis B. Infectious diseases are declining around the globe. An infectious disease is contagious when it spreads through direct bodily contact with an infected person their discharges or an object or surface theyve contaminated.
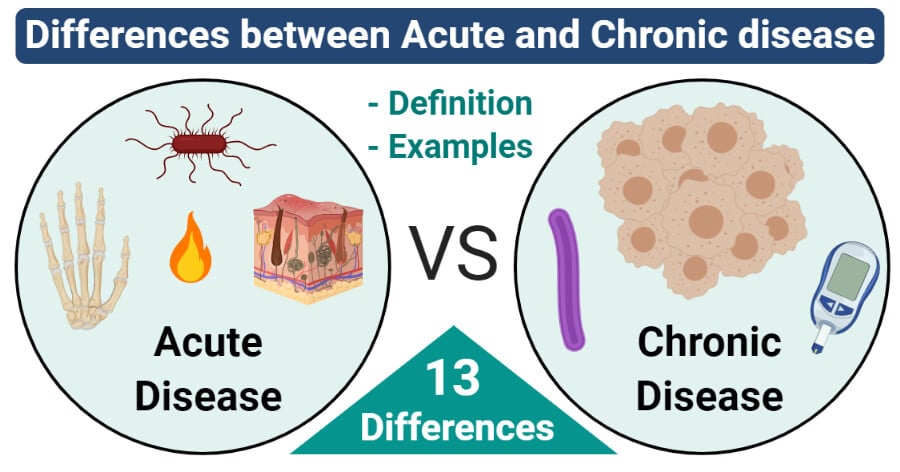
The diseases which occur suddenly and last for a few days are called acute diseases. Finally the World Health Organization states that chronic diseases are not passed from person to person. Chronic and Infectious Diseases.
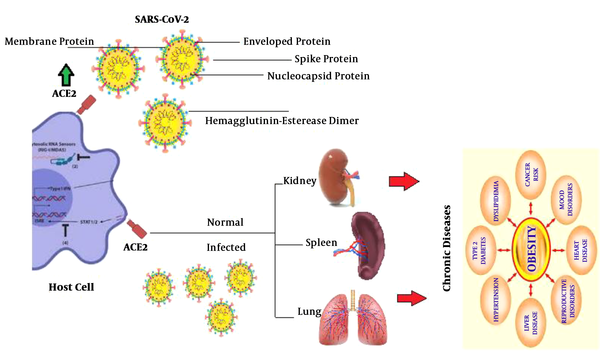
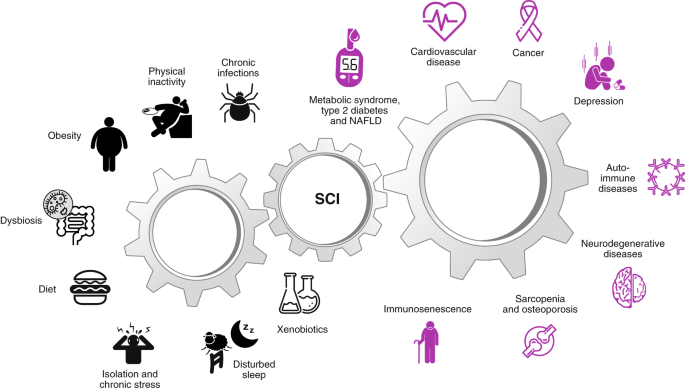
The chronic diseases are those which occur gradually and last for a lifetime. Population has one or more chronic diseases including heart disease cancer diabetes obesity and addiction they can often be prevented and treated successfully. First an infectious agent produces chronic illness or long-term disability through progressive tissue pathology or organ decompensation eg HBV-associated CLD and HCC attributable to direct.
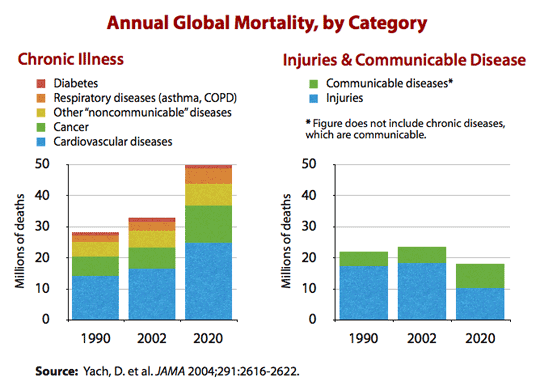
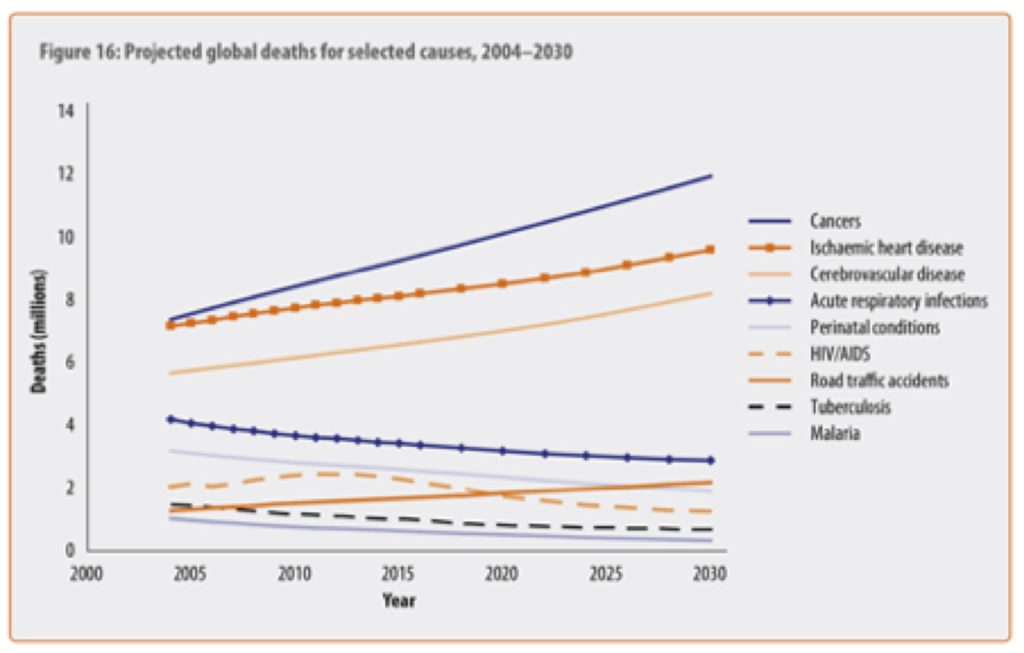
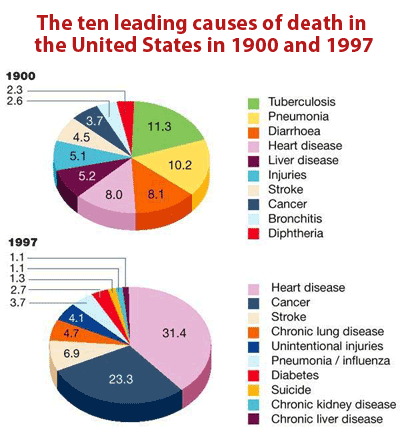
Acute and chronic diseases are caused by infectious agents. Chronic diseases are projected to take the lives of 35 million people in 2005 which is double the estimate for all infectious diseases combined. Common chronic diseases include arthritis asthma cancer COPD diabetes and viral diseases such as hepatitis C and HIVAIDS.
At that time the assumed cause of peptic ulcers was environmental variables such as chronic stress but was alternatively determined to be Helicobacter pylori an infectious. A paucity of tools to detect many agents and the challenges of linking past infectionsometimes decades in the pastwith present chronic illness perpetuated the idea that most infectious diseases are acute illnesses and that chronic diseases have noninfectious causes. Of these chronic disease deaths 16 million will occur in people under 70 years of age and 80 will occur in low and middle income countries.
Diseases are frequently referred to as communicable or non-communicable. LONDON Reuters - The world is caught in a perfect storm of rising rates of chronic disease persistent infectious diseases and public health failures that.
The chronic diseases are those which occur gradually and last for a lifetime.
AIRs work draws on effective strategies that aim to prevent these diseases increase access to quality care and. A paucity of tools to detect many agents and the challenges of linking past infectionsometimes decades in the pastwith present chronic illness perpetuated the idea that most infectious diseases are acute illnesses and that chronic diseases have noninfectious causes. Acute and chronic diseases are caused by infectious agents. 1 Many chronic diseases have an infectious origin such as cervical cancer human papillomavirus HPV and liver cancer hepatitis B. Though there have been observed associations between chronic disease and infectious disease since the beginning of epidemiological research increased emphasis on this relationship began in the late 1970s when new associations between specific infectious and chronic diseases were observed. One classification is based on cause infectious and noninfectious diseases while the second is based on effect chronic and acute diseases. Infectious illnesses tend to occur suddenly and be short-lived. At that time the assumed cause of peptic ulcers was environmental variables such as chronic stress but was alternatively determined to be Helicobacter pylori an infectious. This transmission is typically very easy and results from close casual contact.
While infectious disease still remains a major problem in many countries chronic diseases including such noncommunicable conditions as cardiovascular disease cancer diabetes and respiratory disease are now the major cause of death and disability not only in developed countries but also worldwide. Communicable diseases are infectious diseases. Chronic diseases often develop over many years and last a long time. An infectious disease is contagious when it spreads through direct bodily contact with an infected person their discharges or an object or surface theyve contaminated. Acute and chronic diseases are caused by infectious agents. Of these chronic disease deaths 16 million will occur in people under 70 years of age and 80 will occur in low and middle income countries. One classification is based on cause infectious and noninfectious diseases while the second is based on effect chronic and acute diseases.




















.png)








Post a Comment for "Chronic Disease Vs Infectious Disease"