What Are Target Cells In The Endocrine System
What are target cells in the endocrine system. Exocrine glands not part of the endocrine system secrete products that are passed outside the body. It has a role in hormone production as well as in digestion. Alpha cells which secrete glucagon beta cells which secrete insulin and delta cells which inhibit the secretion on glucagon and insulin.
Describe the features of the endocrine system for control in the example given. Both type I and type II DM are characterized by lack of or low levels of insulin. A group of cells that have receptors embedded in the plasma membrane that are complementary in shape to specific hormone molecules.
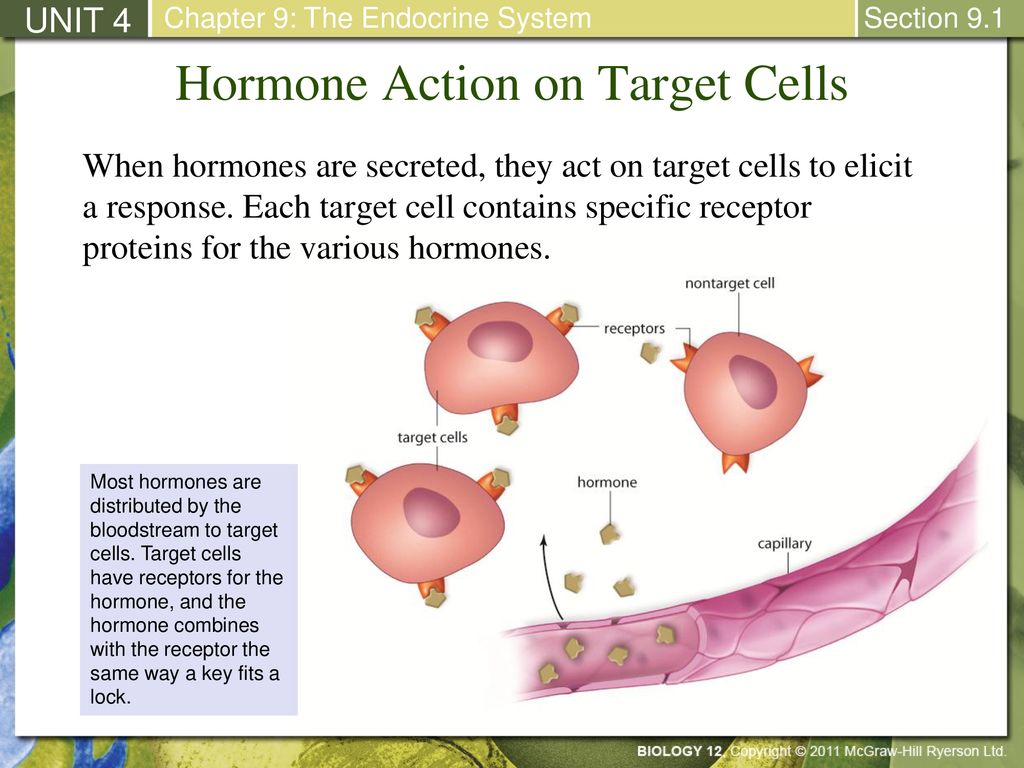
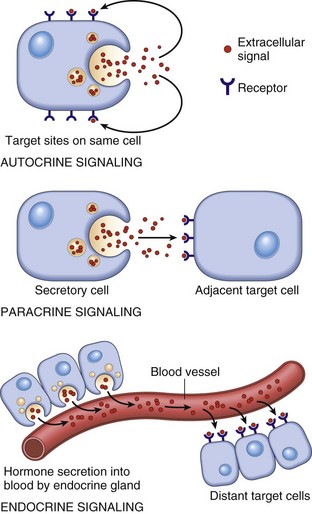
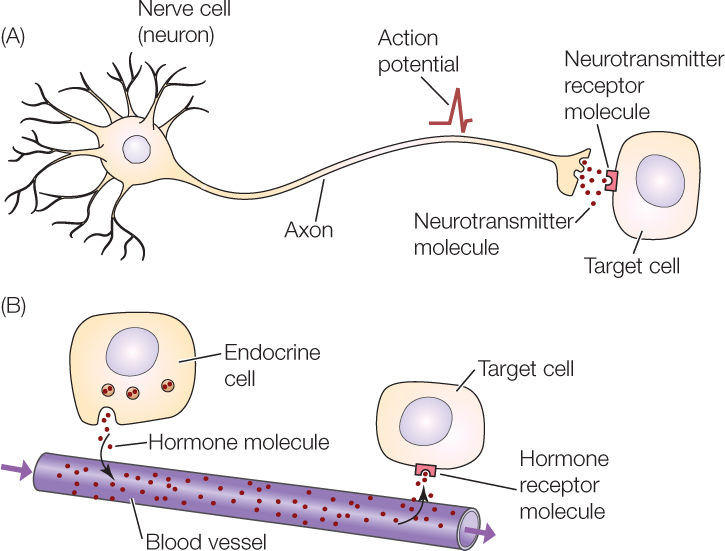
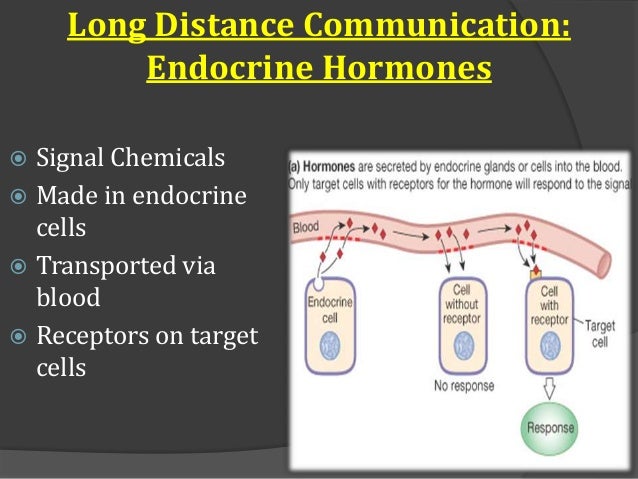
Hormones can be thought of as chemical messages. The target cells for each hormone are characterized by the presence of certain docking molecules ie receptors for the hormone that are located either on the cell surface or inside the cell. There are three types of endocrine cells.
2 rows What is a target cell in the endocrine system. The body produces autoantibodies that destroy the pancreatic beta cells in type I DM. Receptor target cell skeletal muscle Hormone will not bind to cells that are not target cells Figure 281.
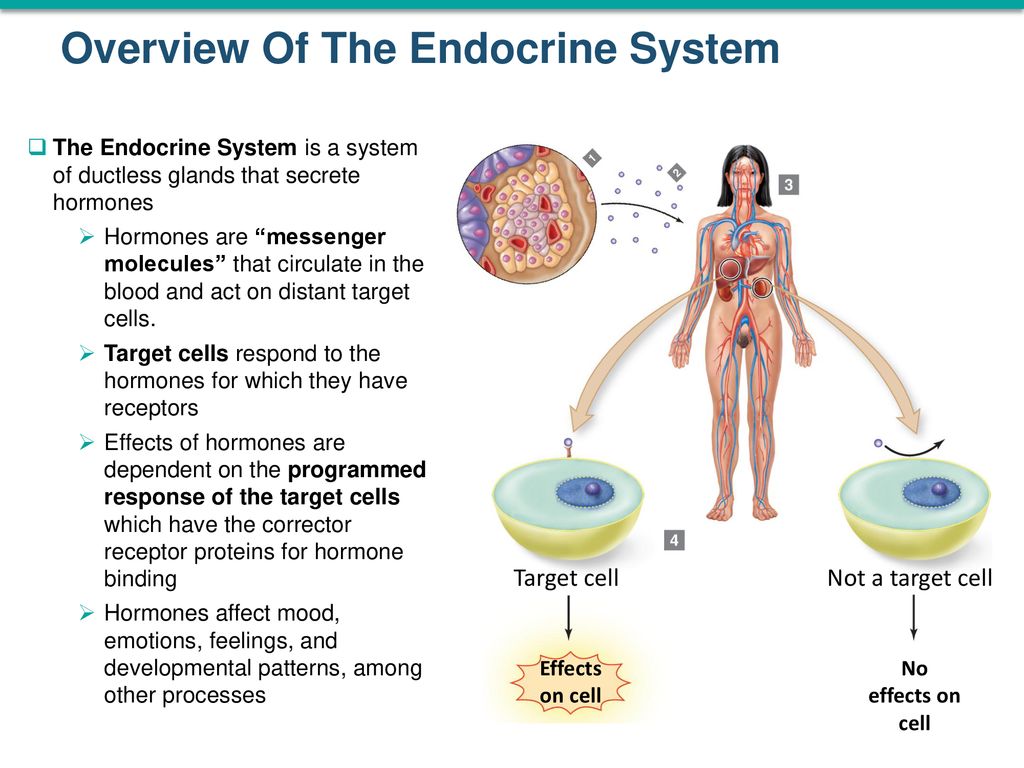
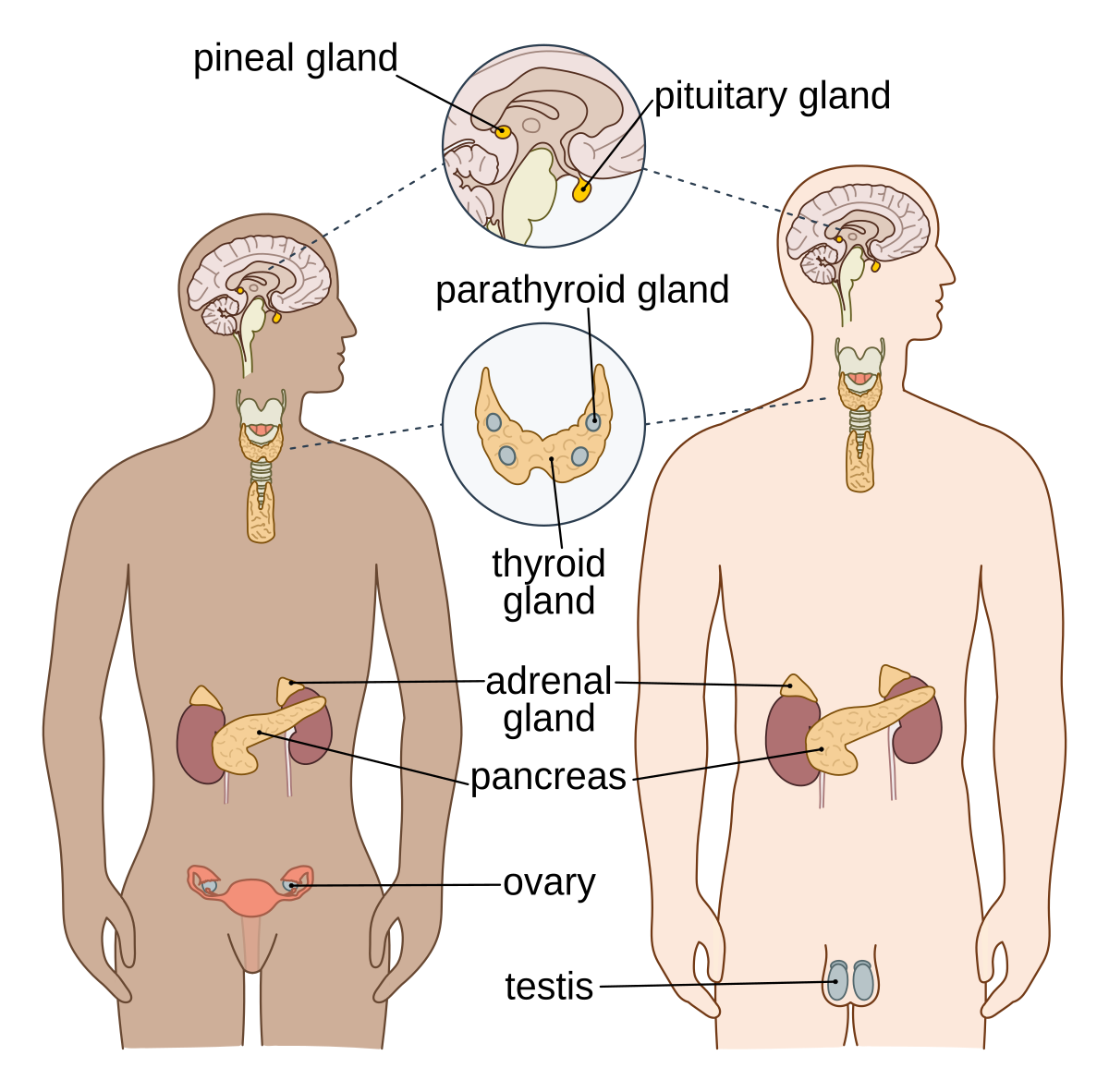
Exam 2 Endocrine The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. The major glands of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus pituitary thyroid parathyroids adrenals pineal body and the reproductive organs ovaries and testes.
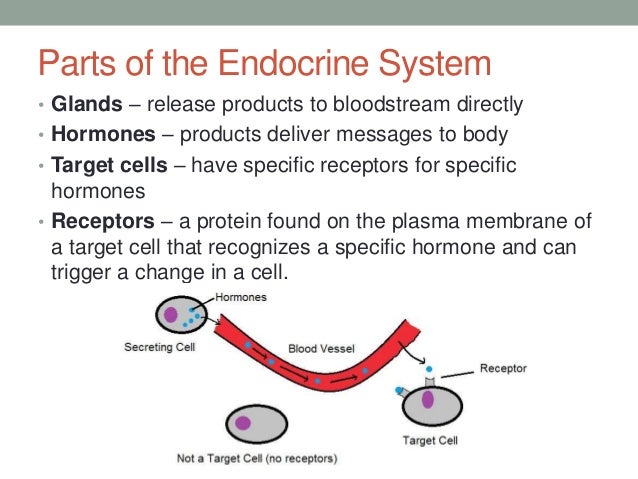
From the blood stream the hormones communicate with the body by heading towards their target cell to bring about a particular change or effect to that cell. Only these cells will respond to the specific hormone. Hormones and Target Cells 1.
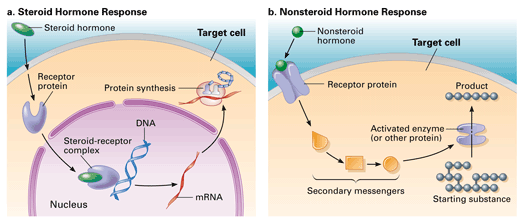
All hormones have a target and target cells have specific receptors on the cell membrane for that hormone. The interaction between the hormone and its receptor triggers a cascade of biochemical reactions in the target cell that eventually modify the cells function or activity.
Glucagon increases the blood glucose level by stimulating the liver causing convert Glycogen into Glucose sugar.
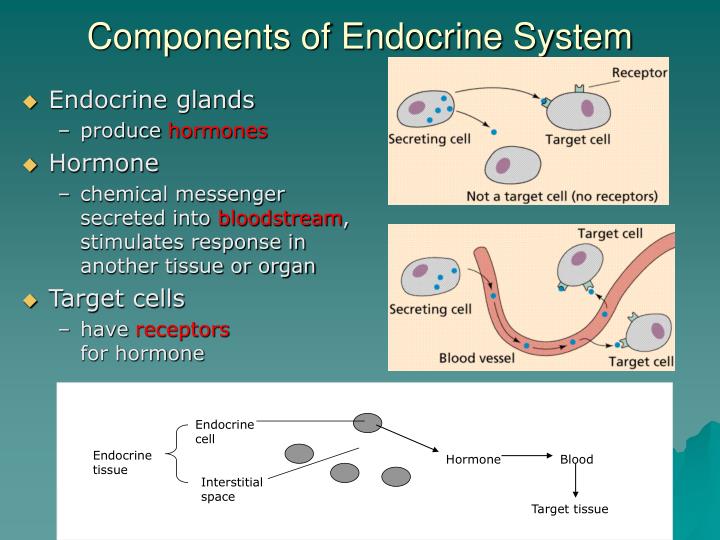
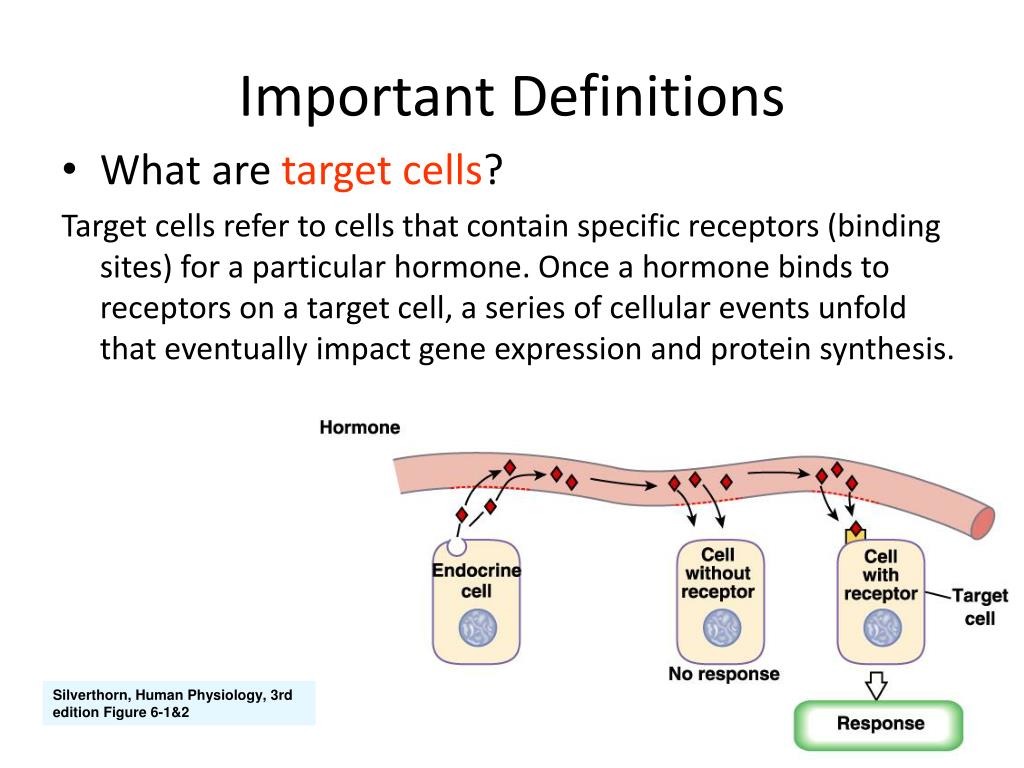
In other words a particular cell is a target cell for a hormone if it contains functional receptors for that hormone and cells which do not have such a receptor cannot be influenced directly by that hormone. The endocrine system is made up of a complex network of glands which are organs that secrete substances. Sources of hormones in humans the endocrine system Fig. Both type I and type II DM are characterized by lack of or low levels of insulin. Exam 2 Endocrine The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream. 2 rows What is a target cell in the endocrine system. The body produces autoantibodies that destroy the pancreatic beta cells in type I DM. Receptor target cell skeletal muscle Hormone will not bind to cells that are not target cells Figure 281. All hormones have a target and target cells have specific receptors on the cell membrane for that hormone.
All hormones have a target and target cells have specific receptors on the cell membrane for that hormone. Various hormones in the endocrine system control growth metabolism and the production of reproductive cells among other things. All hormones have a target and target cells have specific receptors on the cell membrane for that hormone. Receptor target cell skeletal muscle Hormone will not bind to cells that are not target cells Figure 281. 2 rows What is a target cell in the endocrine system. The body produces autoantibodies that destroy the pancreatic beta cells in type I DM. Endocrine gland-negative feedback mechanism-produce hormone - travel via blood- target specific cells organs expand these bullet points.

























Post a Comment for "What Are Target Cells In The Endocrine System"